Basic Troubleshooting of Brocade SAN Switch
1. Login Procedure for the SAN switch
Please
follow the below steps whenever you suspect issue with Switch ports:
- login jumpstation using
jumpstation accounts
- Login to
Storage management server (SMA)
- Telnet to switch with admin
privileges (Eg: user name=admin; Password=password)
2. Checking
the port status on the SAN switch
a. Once logged into
the switch with admin privileges, execute the command Switchshow
b. The output of the
command will be as shown in the following screenshot
c. The status of the
port will be either of the following states as shown in the next page
- Port should be online (Either
F port or E port) and if the port is not online, it will be having one of
the statuses mentioned above. Please make a note of necessary actions that
have to be taken for the following most common states:
No_Module: There is no SFP
installed and hence this port needs SFP to accept logins from any devices
connected to this port
No_Light: There is no
light coming from the node. This means there is some physical problem like
cable, SFP, even HBA might be faulty
No_Sync: This means there
is light and it is not physical problem. This is something to do with
configuration on the switch (like port speed not matching)
In_Sync: This means the
node HBA and switch ports are in synchronization but there could be driver
issue on the Host HBA. That is why the port is not coming online
Laser_flt: This means
defective GBIC/SFP. Replace them
Port_Flt: This means port
has been marked faulty (defective GBIC/SFP, Cable or device)
Online: The healthy port is always online
- After login
to switch console, execute the command Porterrshow to know the crc errors for the ports
- The output of the command will be as
shown in the following screenshot
- If the there are more CRC errors, we may have to replace the SFP. But before replacing SFP clear the port statistics by executing the following command
portstatsclear <slot number/port number>
- After this, monitor the port for 24 hours and if CRC errors go on increasing, replace the SFP.
4. Checking
whether switch port went offline
- After login to switch
console, execute the command fabstateshow
to know whether the port went offline/online as shown in the below
screenshot
- In the below example, the
port 7 went offline and came back online
5. Checking
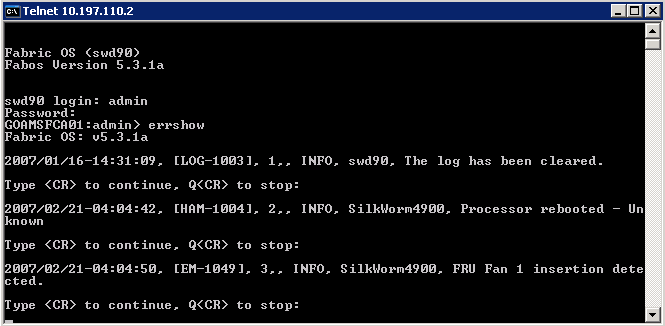
the switch error log
- After login to switch
console, execute the command errorshow
to see any error messages in the switch log
- Please go on entering till
the log for the required date is displayed
- After login to switch
console, execute the command nodefind
to know the physical location of the device in the fabric, alias of
the device and many more details of the device
- In the above screenshot, the red
mark gives the FC address of the port (PID)
- Make note of PID which will
give the location of the device. In the above screenshot, it is 292c00. This is hexadecimal number
where first two digits gives the domain id, next two digits give the port
number and last two digits are always zero in case there is no loop device
in the fabric. For more details please refer to appendix
- Yellow mark gives the type of
HBA, model of HBA, firmware version of the HBA. In this example, this
Emulex HBA model – LP1050 with Firmware version (1.91A5)
- Green colour gives the port
number where node is connected
- Blue colour gives the alias
of the node in the zone
7. How to
find out Domain id of all the switches in the fabric
- After login to switch
console, execute the command fabricshow
to know the domain id of all the switches in the fabric as shown in
the below screenshot
- In the above screenshot, the
first column marked with red colour gives the domain id of all the
switches in the fabric
- Yellow mark where there is
mark (>) indicates the principal switch in the fabric
- Login to Storage management
server (SMA)
- Open putty by clicking the
icon .
- The Putty program will open as shown in the screen shot below
d.Click on session and mention the IP address of the switch & connection type (By default SSH) screenshot below:
- Click on Logging and select all session output as shown below:
- Click on browse to specify
the file name and its path where the output is dumped
- Click on open to open the
console
- Specify the user name and
password
- Once logged into switch
console, execute the command supportshow
- After this command is
completely executed, exit the console of the switch by entering the
command exit
- Find the output file
generated from putty and send it to HPRC for further analysis
9. Appendix
This
appendix covers the concept of addressing mode used in SAN.
PID FORMATS
THE FORMAT OF A 24-BIT ADDRESS IN NATIVE
MODE
XX1YZZ
XX is a value between 0x1 to 0xef
inclusive (Domain ID 1-239 in decimal)
The “1” means Native Mode
Y is the port number 0x0 to 0xf (0-15
decimal)
ZZ is the AL_PA for a loop device or 00
for an F_Port
THE FORMAT OF A 24-BIT ADDRESS IN CORE
PID MODE
XXYYZZ
XX is a value between 0x1 to 0xef
inclusive (Domain ID 1-239 in decimal)
YY is the port area
ZZ is the AL_PA for a loop device or 00
for an F_Port
THE FORMAT OF A 24-BIT ADDRESS IN
EXTENDED EDGE PID MODE
XXYYZZ
XX is a value between 0x1 to 0xef
inclusive (Domain ID 1-239 in decimal)
YY is the port area + 0x10, wrapping at
0x7f
ZZ is the AL_PA for a loop device or 00
for an F_Port










Refurbished and Used Ip Phone Supplier - Informative! We help businesses save costs with reliable pre-owned servers.
ReplyDelete